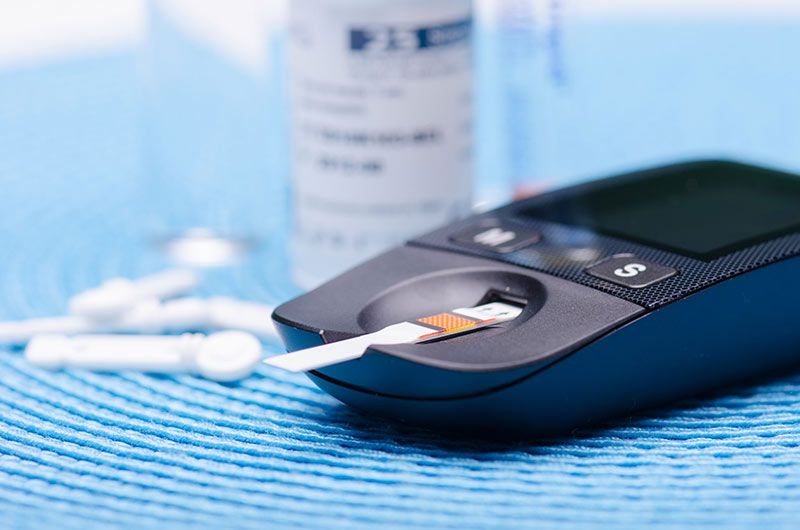
Glucometer Accuracy – US FDA Tightens its Grip
Glucometers remain the golden standard for testing blood glucose at home by those living with diabetes. They are compact and highly affordable. However, those living with diabetes frequently notice the difference between the glucometer readings and lab tests. Also they are not sure about glucometer accuracy.
Difference between lab test results and glucometers occur due to numerous reasons, as glucose levels may change in a short time. However, sometimes these differences are just due to the lower accuracy of glucometers. Thus, FDA decided to tighten its grip to make these glucometers more accurate. US FDA rules have global importance, and emerging economies like India often follow its recommendations.
The problem of the glucometer accuracy was long known to FDA, and one of the early reports were published in 2004, and in 2016 US FDA came up with strict recommendations. These recommendations had a significant impact on the industry and on improving the quality of blood glucometers.
So what made US FDA rethink its policies that it created in 2016? Well, US FDA has seen that though nowadays, all blood glucose meters have better accuracy, but still, not all of them are accurate enough due to some lapses in the manufacturing processes. Moreover, some of the glucometers may become less accurate with time, or due to other reasons.
US FDA criteria for Glucometer Accuracy
- In 95% of cases, the variance should not be more than +/- 15%
- In 99% of cases, the variance should not be more than +/- 20%
For clinical blood glucose monitoring systems this requirement is +/-12% and +/- 15%. It means that there is nothing like 100% accuracy. If we compare with clinical glucose monitoring systems, then personal glucometers are reasonably accurate.
In the latest changes, FDA is asking to include the warning not to use personal-use meters and their strips in the clinical settings. These changes come as FDA realizes the heightened risk posed by these systems of spreading certain infections in the clinical setting, though at home things are entirely different.
Link to FDA document about recommendations for clinical glucometers.
Also this is the link to FDA’s recommendations for home glucometers.
Other new FDA requirements
These latest changes by FDA have less to do with the glucometer accuracy, and more to do with the manufacturing. Since FDA believes that if manufacturing of medical devices are following the highest of standards they will continue to provide accurate results for long.
Manufacturing process– FDA made it stricter for the manufacturers to maintain information about the lots and other things. Further, there is a change in the way of manufacturing site inspection.
Labeling– There are changes regarding the packing and marking of test strips. Now the FDA demands that there should be more information on the test strips packs. These information must include about lot, production, and accuracy of test strips. It means that in future buyers will be able to compare the accuracy of various blood glucose meters before making a buying decision.
Third party manufacturing– is one of the most critical. Most of the regulatory norms set out by US FDA are applicable in the US only. Those standards are not followed well outside the US. Moreover, people often use third-party strips that are not made by following the same strict rules. All this means that if blood glucose meter or strips are produced outside the US by the third party, they may not be very accurate. However, this is going to change. US FDA is going to demand higher quality standards from the third parties too.
Post-marketing scrutiny of glucose meters
Quite often glucometers are accurate in the beginning when the company was getting all the approvals. However, with time quality of the product becomes inferior and devices become less reliable. Thus FDA is also concerned about the post-marketing quality of glucometers. Also FDA is asking to maintain better records about quality testing, lots, and so on.
US FDA is trying to minimize the difference between the pre-market and post-market accuracy of blood Glucometers. FDA wants to make sure that there is no decline in performance of glucometers over the time.
Compliance isn’t mandatory
It is one of the critical things that consumer needs to know. These recommendations or directives by the FDA are non-binding. It means that at the end of the day, it is up to the manufacturer to follow these instructions or not.
From an Indian perspective, it is necessary to understand that no Indian manufacturer is bound to follow the recommendation of US FDA. Nonetheless, many prestigious manufacturing companies try to follow these instructions. They operate in numerous countries, and want to ensure that their product is of the highest quality. It means that when choosing a medical device like glucometer, one may see how much does manufacturer comply with the latest FDA norms for glucometer accuracy.











Nice article